Modulation is a very important concept in electronics and telecommunication. It occurs when we vary one or more properties of a carrier signal with a modulating signal. Modulation is of different types. When we modulate an analog signal, it is called analog modulation and when we modulate a digital signal, it is called digital modulation. Modulation mainly occurs when the characteristics of input signal i.e. amplitude, frequency, and phase are improved with reference of the carrier signal. For transmission purposes, digital signals are always preferred over analog signals. This is because of the fact that analog signals may suffer from noise, distortion and interference effects. However, these possibilities are comparatively less in the case of digital signals. Digital signals have two voltage levels i.e. either high or low while in case of an analog signal, the voltage is continued. If the amplitude of the carrier wave is varied with respect to that of the message signal, then this type of modulation is called Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Shift Keying is a type of amplitude modulation in which digital signal is represented as a change in the amplitude of a carrier wave.
Definition: ASK is a type of modulation where the digital signal is represented as a change in amplitude. In order to carry out amplitude shift keying, we require a carrier signal and a binary sequence signal. It is also known as On-Off keying. This is because the carrier waves switch between 0 and 1 according to the high and low level of the input signal.

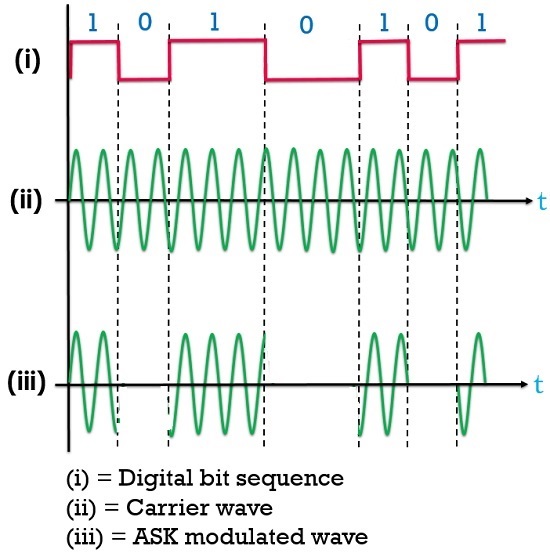
Amplitude Shift Keying
Here, (i) represents the digitalized input sequence or message signal (ii) represents the carrier wave of higher amplitude and frequency and (iii) represents the ASK modulated wave.
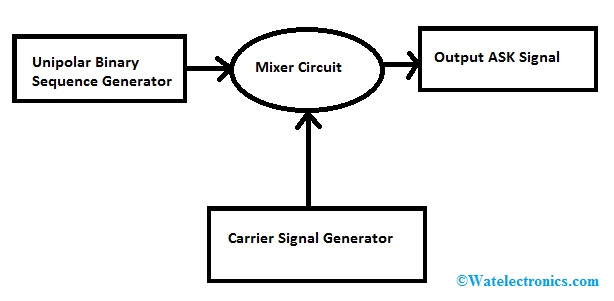
ASK Block Diagram
In amplitude shift keying, the phase and frequency of the carrier wave are maintained at a constant level and only its amplitude is varied in accordance with the digitalized modulating signal. It is associated with two levels only. However, there can be multiple levels of signal elements as well. Here, the carrier wave signal has a greater amplitude range than the binary sequence signal.
The carrier signal is used to transmit the message signal over long distances. As a result, the characteristics of the carrier signal are taken higher than that of the message signal so that the binary input signal can be transmitted to long distances without any kind of distortion. We increase the characteristics by multiplying the binary input signal with the carrier signal of higher frequency.
Generation of ASK signal
The entire setup consists of a signal generator that can produce a high-frequency sinusoidal waveform, a bandpass filter, and a digital input signal. When the bit is 1, the voltage is high and the switch is closed. This allows the carrier wave to get transmitted. However, when the bit is 0 i.e. the voltage level is low, then the switch is open thus restricting the carrier wave. That is why the output signal appears only at higher voltage levels. The band limiting filter is used to reshape the pulse in accordance with the characteristics of the filter.
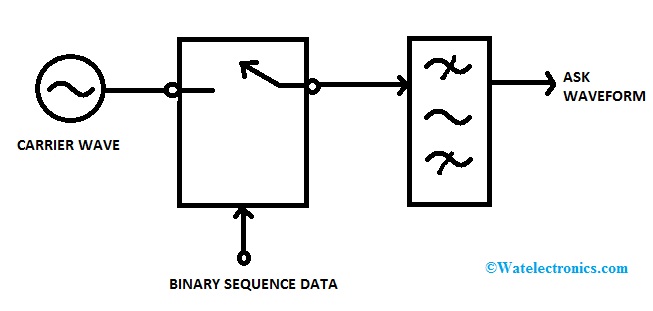
Generation of Amplitude Shift Keying Signal
We can design the ASK modulation circuit using a 555 timer IC in an astable mode. We can vary the carrier signal by using R1, R2 and C. We can calculate the carrier frequency using the formula. We will apply the input digital binary sequence at pin 3 and the modulated wave will be generated at pin 3.
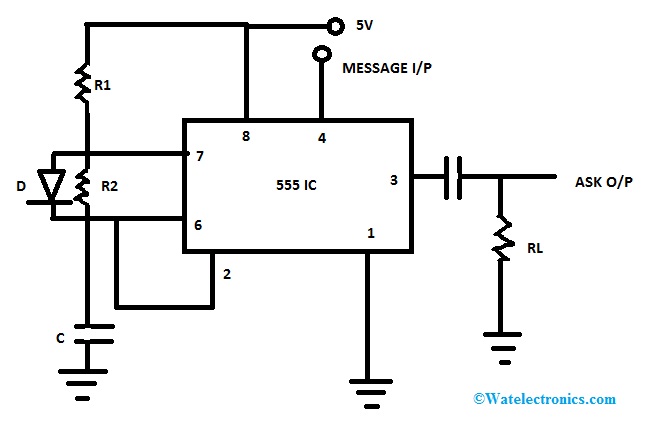
Amplitude Shift Keying Circuit Diagram
Demodulation is the process by which we can reconstruct the original signal at the receiver end. The input signal is reproduced at the output stage of the receiver. ASK detection is of two types:
In this process, the carrier signal at the receiver end is in the same phase and frequency as the replica carrier signal. The signal received at the receiver stage is passed through a low pass filter to eliminate any kind of distortion and noise. The attenuation can be recovered. After that, the signal is transmitted to the circuit where it is converted to digital form. Then, at each level, we compare the digital signal voltage with the reference voltage and in this way, we can reconstruct the original signal.
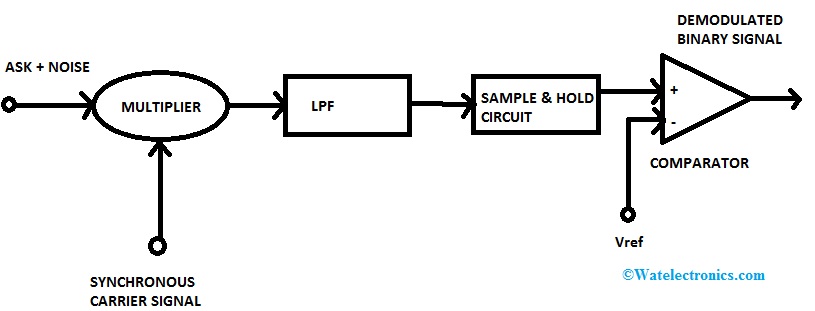
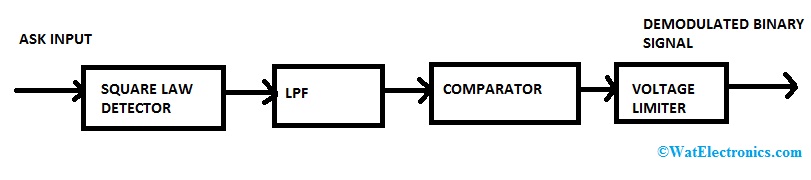
In the case of noncoherent ASK detection, the carrier signal at the transmitter stage and the receiver stage do not have the same phase. This is why it is called asynchronous detection. This process requires a square-law device. The output signal which we get from the square-law device is transmitted to the low pass signal which reconstructs the original signal.
Some of the important applications of ASK has been mentioned below:
1). How are binary values represented in amplitude shift keying?
In ASK, binary values 0 and 1 are represented as low and high voltages. When the binary value is 1, the switch is closed and the signal can pass through and when the binary value is 0, the switch is closed.
2). Why is ASK called on-off keying?
ASK is also called on-off keying because, in the case of ASK, the carrier waves continuously switch between 0 and 1 according to the high and low level of the input signal.
3). Which is called on-off keying?
Amplitude shift keying is also known as on-off keying.
4). What are FSK and ASK?
ASK is amplitude shift keying and FSK is the frequency shift keying. In ASK, the amplitude of the digital signal is varied while in the case of FSK, the frequency of the digital signal is varied.
5). What do you mean by modulation?
Modulation is the process that occurs when we vary one or more properties of a carrier signal with a modulating signal.
Thus, this is all about an overview of amplitude shift keying, block diagram, circuit and its working with applications. Here is a question for you, what are the types of ASK?